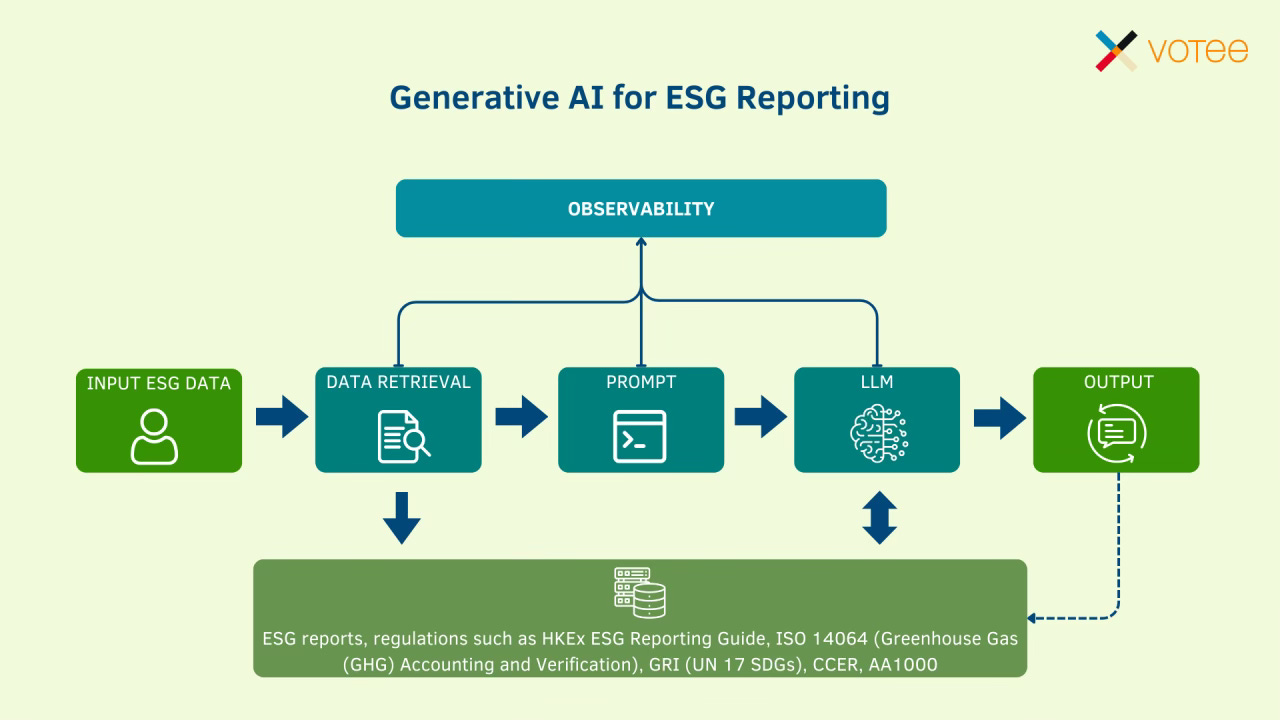
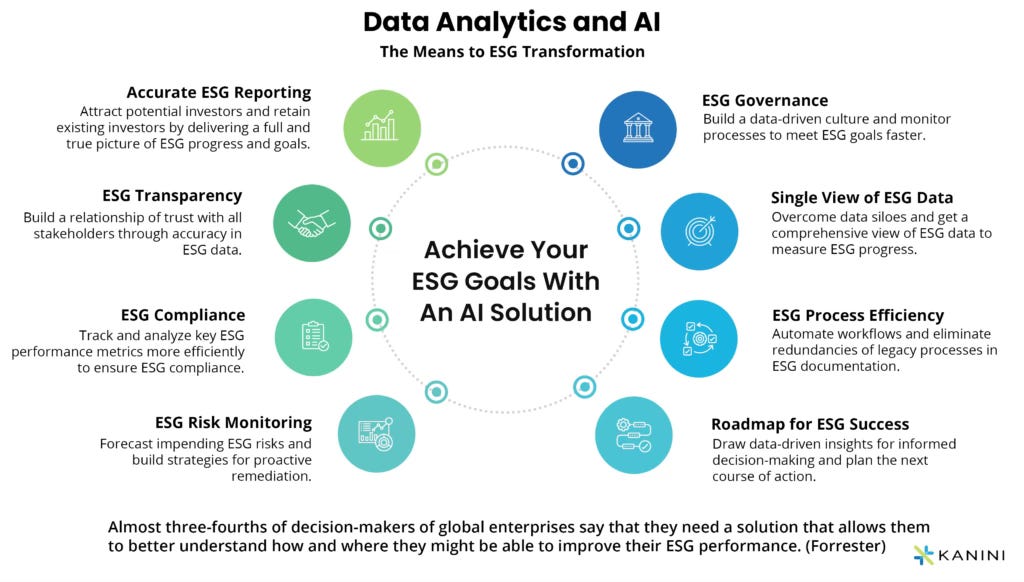
How Artificial Intelligence Is Shaping the Future of ESG: Opportunities and Challenges
As the world increasingly turns its focus to sustainability, social responsibility, and corporate governance, businesses and investors are looking for ways to accelerate progress in these areas. Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI), which is rapidly becoming a game-changer in advancing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. From reducing carbon footprints to driving ethical decision-making, AI has the potential to reshape how organizations operate and how investors make decisions. But with great power comes great responsibility—AI also brings with it challenges and risks that need to be carefully managed. Let’s explore how AI is influencing ESG, the opportunities it presents, and the challenges it brings to the table.
AI and the Environment: A New Era of Sustainability
When it comes to the environment, AI is showing remarkable potential in optimizing how we manage resources and reduce our environmental impact.
AI-powered systems are already helping companies streamline energy use in manufacturing, transportation, and buildings. For instance, algorithms can predict energy demand in real-time, allowing for a more efficient distribution of power, reducing waste, and lowering emissions. In agriculture, AI tools can optimize irrigation practices and crop management, minimizing water usage and pesticide application. AI is also being used to track biodiversity and monitor pollution levels, giving real-time insights into environmental risks.
Beyond monitoring and efficiency, AI is also contributing to carbon reduction strategies. In logistics, for example, AI helps companies optimize routes, reducing transportation emissions. In the renewable energy sector, AI assists in predicting and managing energy flows from solar and wind farms, increasing their efficiency and reliability.
The ability to harness AI for environmental monitoring could be the key to achieving the bold climate targets set by governments and corporations worldwide. However, for AI to truly contribute to sustainability, it must be implemented with an eye toward ensuring that the technologies themselves do not exacerbate environmental issues—like the significant energy consumption of large-scale AI models.
Social Impact: Making Businesses More Inclusive and Equitable
The social aspect of ESG is where AI’s potential to make a real difference is most evident, especially in areas like healthcare, education, and workplace diversity.
In healthcare, AI systems are being used to predict disease outbreaks, improve diagnostic accuracy, and personalize treatments, all of which can dramatically improve health outcomes, particularly in underserved communities. In education, AI-powered platforms are enabling personalized learning experiences for students, offering tailored resources and support that can help bridge gaps in access and outcomes.
AI is also playing a key role in enhancing workplace inclusivity. Machine learning models can help companies identify and mitigate bias in recruitment processes by analyzing historical hiring data and flagging patterns that might result in discriminatory practices. Tools are emerging that can monitor diversity within organizations and identify potential barriers for underrepresented groups. This type of data-driven insight is crucial for organizations striving to meet diversity and equity goals.
However, AI’s role in improving social outcomes must be handled with care. If not properly managed, AI can perpetuate biases in hiring, lending, and even law enforcement, exacerbating existing social inequalities. For instance, if algorithms are trained on biased data, they can reinforce stereotypes or make discriminatory decisions, undermining the very goals they were meant to achieve. The challenge, then, is not only to apply AI in a way that improves social outcomes but also to ensure that it is designed and deployed ethically.
Governance: Ensuring Transparency and Accountability in AI
Governance is where AI intersects with some of the most pressing issues of our time: accountability, transparency, and ethical decision-making. Good governance ensures that AI systems are used in a way that is not only efficient but also aligned with ethical standards and regulatory frameworks.
AI can enhance governance in numerous ways. For example, by automating the monitoring of regulatory compliance, AI can help companies stay on top of changing laws and avoid costly legal penalties. It can also be used to improve financial oversight, identifying anomalies in financial transactions that might indicate fraud or malpractice.
Furthermore, AI can assist companies in making better, data-driven decisions about ESG investments, helping to align corporate strategy with long-term sustainability goals. By using AI to track and analyze ESG metrics across industries, investors can make more informed choices, directing capital toward companies that prioritize environmental protection, social responsibility, and good governance.
But the widespread use of AI in governance raises critical concerns. As AI systems become more complex, ensuring transparency in their decision-making processes becomes increasingly difficult. This "black-box" problem, where AI systems make decisions that are difficult to explain or understand, poses significant challenges for companies and regulators alike. The key to effective AI governance will be developing standards and practices that ensure AI systems remain accountable, fair, and transparent.
The ESG Investment Opportunity: AI as a Tool for Informed Decision-Making
As ESG investing continues to gain traction, AI offers investors powerful tools for identifying and evaluating ESG performance across portfolios. Traditionally, assessing ESG criteria relied heavily on qualitative data and subjective judgment. However, AI's ability to analyze vast amounts of data from multiple sources—such as financial reports, social media, news outlets, and regulatory filings—allows for a more comprehensive and objective assessment of a company's ESG performance.
Machine learning models can analyze these datasets to uncover hidden risks and opportunities related to environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. Investors can use AI to assess whether companies are meeting their sustainability targets, identify potential red flags, and even forecast future ESG trends. This is crucial for making informed, data-driven investment decisions.
Moreover, AI can assist in developing ESG-focused investment strategies by identifying trends in sectors like renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and green technology. This could help investors achieve both financial returns and alignment with their ethical and sustainability goals.
The Challenges Ahead: AI's Risks and Ethical Concerns
Despite the enormous potential of AI in driving ESG improvements, there are significant challenges and risks that need to be addressed.
AI Bias: If not properly managed, AI systems can perpetuate existing biases, especially in areas like hiring, lending, and criminal justice. Companies must invest in training AI models on diverse and representative datasets and continuously monitor them to ensure they are not unintentionally reinforcing inequality.
Data Privacy: AI relies heavily on data, and much of this data is personal or sensitive in nature. Whether it’s health data, employee information, or consumer preferences, privacy concerns are paramount. Striking the right balance between leveraging data for AI applications and protecting individual privacy is critical.
Job Displacement: As AI automates more processes, there’s the risk of job displacement, particularly in sectors where routine tasks are being automated. Companies and governments must prioritize reskilling and upskilling workers to prepare for a future where AI plays an increasingly significant role.
Environmental Impact of AI: As AI models grow in complexity, so too does their energy consumption. The environmental impact of training large-scale AI models, particularly those used in deep learning, is a growing concern. Companies must find ways to optimize AI technologies to minimize their carbon footprint.
Conclusion: The Future of AI and ESG
AI’s role in driving ESG goals is undeniable, offering transformative opportunities for businesses, investors, and society as a whole. From improving sustainability practices to enhancing social equity and strengthening corporate governance, AI has the potential to drive meaningful change. However, its deployment must be handled responsibly, with a focus on fairness, transparency, and ethical considerations.
As AI continues to evolve, its impact on ESG will only deepen. Companies and investors who are proactive in integrating AI into their ESG strategies will be well-positioned to thrive in a world that increasingly values sustainability, ethics, and long-term responsibility.
The question isn’t whether AI will be part of the future of ESG—it’s how we will harness its potential while managing its risks. The answer lies in careful, thoughtful governance that ensures AI becomes a force for good in creating a more sustainable and equitable world.